Inside the Mind: A Deep Dive Into Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a profoundly complex and chronic mental health condition that disrupts a person’s ability to think clearly, manage emotions, make decisions, and relate to others. Those living with schizophrenia often find it difficult to differentiate between what is real and what is not. This disconnection from reality may lead to periods of detachment, emotional flatness, or social withdrawal, especially during interactions that require emotional presence or expressive communication.
Schizophrenia is often likened to a fragmented puzzle—an enigmatic brain condition with crucial pieces missing or scattered. This deeply rooted biochemical disorder can warp perception and skew reasoning. It's almost as though the brain reroutes information through the wrong channels, resulting in distorted beliefs and sensations. Individuals may experience terrifying delusions, vivid hallucinations like hearing disembodied voices, isolating social behavior, and deeply disordered patterns of thinking that make day-to-day life incredibly difficult to navigate.
A Closer Look: Defining Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a severe psychiatric disorder that alters the way a person interprets the world and communicates with it. It interferes with perception, thought, emotions, and behavior.
In the early phases of an episode, subtle changes might occur—things in the environment may begin to feel oddly unfamiliar or distorted. Focus becomes elusive. Conversations become more difficult to follow. Social participation may decline as ordinary activities start to feel exhausting or confusing. As the illness progresses into an active phase, these symptoms can intensify and evolve into full-blown psychosis. Individuals may hear voices that others don’t, or cling to strong beliefs that have no grounding in reality—such as thinking they possess extraordinary abilities or are under surveillance.
Some people experience what's known as a “flattened affect”—a diminished ability to express emotions. Motivation might disappear, mood can swing drastically, and daily responsibilities might suddenly feel impossible to complete. Even after the most severe symptoms subside, lingering challenges like poor concentration or emotional withdrawal may persist for weeks, months, or longer.
One of the most puzzling aspects of schizophrenia is that its course and intensity vary drastically from person to person. Some might only have a single psychotic episode in their lifetime, while others may battle recurring symptoms throughout their lives. Some experience calm, functional periods between episodes; others may struggle with persistent symptoms. Some notice warning signs before each episode; others are blindsided. Despite this variability, one truth holds steady: early diagnosis and intervention often lead to better long-term outcomes.
Key Facts About Schizophrenia
-
Schizophrenia is a lifelong, serious mental illness affecting an estimated 20 million people across the globe.
-
It is marked by severe disruptions in how individuals perceive reality—touching on everything from thoughts and language to emotions and behavior. Hallucinations and delusions are hallmark symptoms that can deeply disturb a person’s sense of reality.
-
The condition often leads to significant functional impairment, limiting a person’s ability to succeed in academic, work, or social environments.
-
Individuals with schizophrenia are at a substantially higher risk—2 to 3 times more likely than the general population—to die prematurely. These early deaths are usually due to untreated or preventable physical illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes, and infectious conditions.
-
Widespread stigma and discrimination remain major challenges. People with schizophrenia often face human rights violations, including barriers to housing, employment, and social inclusion.
-
Schizophrenia is manageable. Effective treatments, including antipsychotic medication and psychosocial support, help many lead more stable and fulfilling lives.
-
Integrative care models that combine medical support with assisted living services, supported housing, and structured employment assistance have shown great success in helping individuals achieve stability and independence.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Schizophrenia is classified as a psychotic disorder, meaning it primarily affects how a person perceives and interprets reality. Its symptoms can be divided into several broad categories, and while the intensity varies, the underlying patterns often share common threads:
-
Hallucinations – These involve sensing things that aren't present. Most commonly, people hear voices, but hallucinations can also affect sight, touch, smell, or taste.
-
Delusions – These are deeply held, false beliefs that defy logic or cultural norms. A person might believe they’re being tracked by government agencies, that they possess divine powers, or that random events have special meaning for them.
-
Unusual or Erratic Behavior – This may include disorganized movement, odd rituals, talking or laughing to oneself, lack of self-care, or unpredictable emotional responses.
-
Disorganized Speech – Communication may become jumbled, incoherent, or entirely nonsensical. It’s not uncommon for a person to jump from topic to topic with no logical connection.
-
Emotional Disturbances – There can be a disconnection between internal feelings and outward expressions. A person might speak of sorrow while showing no emotion, or react minimally to emotionally charged situations. Apathy, or lack of motivation, is also common.
Scope and Consequences
Though schizophrenia affects fewer people globally compared to conditions like anxiety or depression, its impact is disproportionately profound. It affects around 20 million individuals worldwide, making it one of the most disabling psychiatric illnesses.
Notably, men often begin to exhibit symptoms earlier than women, with onset typically occurring in late adolescence or early adulthood.
Living with schizophrenia presents numerous obstacles. It can significantly disrupt educational progress, strain personal and professional relationships, and interfere with a person’s ability to maintain steady employment. On top of that, co-occurring physical illnesses—especially those tied to poor lifestyle habits or medication side effects—can severely shorten life expectancy.
Discrimination and misunderstanding continue to haunt those with schizophrenia, often denying them access to vital services, dignity, and social inclusion.
What Triggers Schizophrenia?
The scientific community has yet to pinpoint a single, definitive cause of schizophrenia. Instead, the condition appears to emerge from a complex interplay of biological and environmental factors:
-
Genetics – Individuals with a family history of schizophrenia have a significantly higher risk, although having a relative with the illness doesn’t guarantee someone will develop it.
-
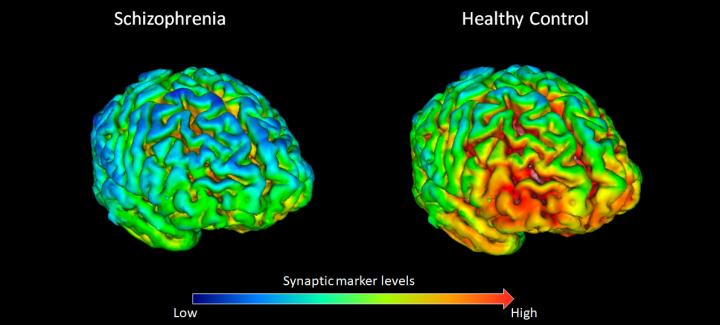
Brain Chemistry and Structure – Irregularities in brain chemicals like dopamine and glutamate, as well as observable structural differences in certain brain regions, are often associated with the condition.
-
Environmental Influences – Factors like exposure to viruses before birth, childhood trauma, complications during birth, or intense psychosocial stress can all contribute to risk.
Researchers continue to explore how these elements combine to alter brain development and function in ways that ultimately manifest as schizophrenia.
Who Is Vulnerable to Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia does not discriminate. It can touch the lives of individuals from any background, culture, or region. However, the typical onset of symptoms often occurs during the late teenage years or early adulthood. Interestingly, males usually begin to show signs of the disorder earlier than females—sometimes as young as the late teens, while females may not present symptoms until their twenties or even later.
What makes schizophrenia particularly unpredictable is how differently it can manifest from person to person. While one individual might experience a sudden and severe episode of psychosis, another might encounter a slow, subtle decline in functioning over time. There is no clear formula to predict who will develop schizophrenia or how it will evolve.
Though the exact cause remains elusive, most researchers agree that a combination of genetic inheritance, brain development abnormalities, and significant life events likely play a role. For instance, someone with a biological predisposition may never develop the illness unless triggered by overwhelming stress, trauma, or environmental challenges during crucial developmental windows.
What Steps Can Be Taken to Manage It?
While there is currently no known cure for schizophrenia, people can recover—or at the very least, build fulfilling and functional lives while managing the condition. Recovery doesn't always mean a full remission of symptoms. More often, it’s about finding the right strategies and support systems to live as independently and meaningfully as possible.
Most people benefit from a tailored mix of treatment options. Here are the primary approaches:
Inpatient Care for Acute Episodes
When symptoms escalate and a person loses touch with reality, hospitalization may be necessary—especially for safety, stabilization, and diagnostic clarity. These stays help care teams assess the best course of treatment. Before discharge, healthcare professionals often help patients build a recovery roadmap that includes doctors, therapists, and support workers.
Medication
Antipsychotic medications are a central tool in managing schizophrenia. They can reduce or even eliminate distressing symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions. These medications can be life-changing for many—but they don’t work overnight, and finding the right medication often involves trial and error.
Moreover, all medications come with potential side effects—ranging from mild fatigue or weight gain to more serious complications. That’s why it’s crucial to have ongoing, honest conversations with healthcare providers. Patients should feel empowered to speak up about how a drug affects them, and clinicians should always be open to adjusting treatment accordingly.

Therapy and Psychosocial Support
Therapy can be a powerful companion to medication. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), for example, helps individuals reframe harmful thinking patterns and learn coping mechanisms. Therapy also improves mood regulation, builds insight into symptoms, and strengthens decision-making skills.
Beyond traditional therapy, schizophrenia can interfere with educational, occupational, and social development. That’s where professionals like occupational therapists and social workers step in. They provide hands-on assistance with daily tasks, help build routines, offer employment guidance, and connect people to community resources like transportation, housing, and financial assistance.
Another important aspect of treatment is relapse prevention. Individuals can be taught to identify personal warning signs—whether it’s insomnia, irritability, or withdrawal—so that interventions can begin early and reduce the length and severity of episodes.
Self-Care and Lifestyle Habits
Wellness isn't just clinical—it’s also deeply personal. Developing simple, healthy habits can offer surprising relief. These may include:
-
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule
-
Eating nourishing meals
-
Engaging in physical activity
-
Practicing mindfulness or spiritual rituals
-
Participating in hobbies and creative outlets
-
Reconnecting with friends or trusted loved ones
Although schizophrenia can make people feel disconnected and alone, meaningful relationships are still possible—and they’re often crucial to healing. Many individuals report that joining peer support groups or participating in group therapy helps normalize their experiences and ease isolation.
Helping a Loved One with Schizophrenia
Providing support to someone with schizophrenia can be emotionally challenging and, at times, confusing. Their behavior may seem irrational, unpredictable, or even frightening. Understandably, friends and family often feel overwhelmed, frustrated, or unsure about how to help.
But support truly matters—and love, patience, and informed action can make a tremendous difference. Here's how to offer that help in a way that empowers both you and your loved one:
-
Educate Yourself: The more you understand about schizophrenia, the better prepared you'll be to offer meaningful support without judgment or fear.
-
Adjust Expectations: Schizophrenia can impair the ability to think clearly or respond in expected ways. Tasks that seem routine may be unusually difficult for someone with the condition. Practice empathy, and avoid placing blame when things don't go as planned.
-
Communicate Effectively: Choose calm, quiet spaces for conversation. Speak slowly, clearly, and simply. If the person is struggling with delusions or hallucinations, avoid confrontation. Instead of challenging their beliefs, focus on the emotions those beliefs are stirring up.
-
Ask How to Help: Sometimes, simply asking “What can I do for you today?” goes a long way. Help with meals, housework, or attending appointments may be deeply appreciated.
-
Crisis Planning: When your loved one is doing well, talk together about how to manage future episodes. Discuss early warning signs, emergency plans, and what kind of help they would want during a crisis. Write this down in a shared plan and make sure the care team has a copy.
-
Explore Support Resources: Mental health organizations, care networks, and government programs often offer assistance to caregivers, including counselling, education programs, and financial planning tools like the Registered Disability Savings Plan.
-
Set Healthy Boundaries: You cannot pour from an empty cup. Supporting someone with schizophrenia can be draining, so it's essential to protect your own mental health. Seek your own support group or therapist if needed. It's not selfish—it’s survival.
-
Focus on Realistic Hope: While recovery looks different for everyone, many people with schizophrenia do improve over time. Encourage progress, celebrate small victories, and stay open to what’s possible.